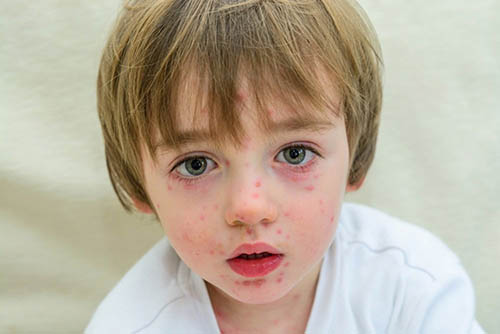
Основным проявлением заболевания, независимо от возраста пациента, становится образование на поверхности кожи гнойных элементов, имеющих характерную округлую форму и шелушащуюся поверхность. В зависимости от размеров патологического очага, их количества и зоны распространения различают клинические формы заболевания.
Причины
Нарушение целостности кожного покрова (для проникновения инфекции достаточно микротравмы или потертости).
Изменение местного иммунитета.
Нарушение активности иммунной системы организма в целом.
В организм ребенка микроорганизм может попасть контактно-бытовым путем – инфекция передается через посуду, одежду, при бытовых контактах, через игрушки, а также через пыль, в которой содержаться стрептококки. В жаркое время года инфекция может передаваться насекомыми, которые на своих лапках переносят возбудителей.
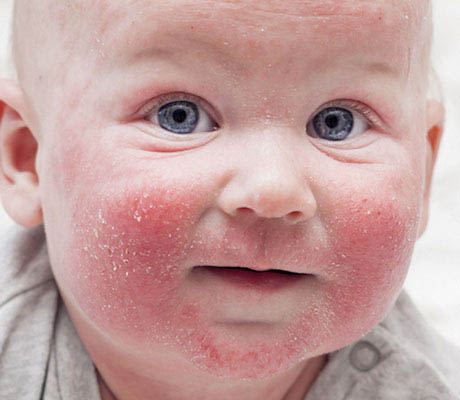
Симптомы
Появление на поверхности кожи небольших пузырьков, наполненных прозрачной, но быстро мутнеющей жидкостью – чаще всего на лице, спине, конечностях, нижней части туловища.
Кожный зуд (часто возникает нестерпимое жжение).
Пигментация кожи на месте «старых» очагов заболевания.
Общее недомогание – нарушение самочувствия, вялость, слабость, отсутствие аппетита.
Стрептодермию можно легко перепутать с крапивницей, атопическим дерматитом, отрубевидным лишаем, пиодермиями и экземой, поэтому ни в коем случае не занимайтесь самолечением. Чтобы получить своевременное лечение, обратитесь к специалисту для быстрого диагностирования болезни.
Профилактика
Соблюдать правила личной гигиены.
Питаться пищей с высоким содержанием витаминов.
Закаляться, вести здоровый образ жизни.
При повреждениях кожи, даже незначительных, тщательно промывать и обрабатывать ранку. Равномерно распределять нагрузку, избегать стрессовых ситуаций.
Препараты для терапии
Стрептодермия у детей лечится достаточно хорошо и быстро, если все делать правильно. Распространенная ошибка родителей – прекращать лечение сразу, как только появятся признаки улучшения. Курс лечения, назначенный врачом, должен быть завершен полностью в обязательном порядке.