Общие сведения
Бородавки — гипертрофированные участки эпителия, как правило, возникающие вследствие инфицирования папилломавирусом. Представляют собой доброкачественные образования на коже или слизистой оболочке. Чаще появляются у детей и подростков, имеющих неокрепшую иммунную систему.
Бородавки могут быть единичные или множественные, овальные или круглые, светлее или темнее окружающих тканей. При отсутствии лечения способны увеличиваться в размере и доставлять дискомфорт.
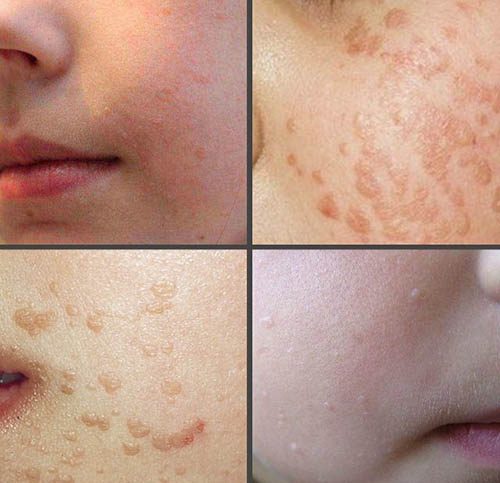
Причины бородавок
Основная причина бородавок у детей — вирус папилломы. Малыши и подростки заражаются этим возбудителем контактным путем через предметы быта, личной гигиены, одежду и белье. Инфицирование происходит в общественных местах, в транспорте, на игровых площадках. Возможна передача микроорганизмов от матери ребенку во время беременности.
Попадая на кожу, вирус проникает в организм через микротрещины, ранки. На протяжении длительного времени заболевание может никак не проявляться.
Диагностика бородавок
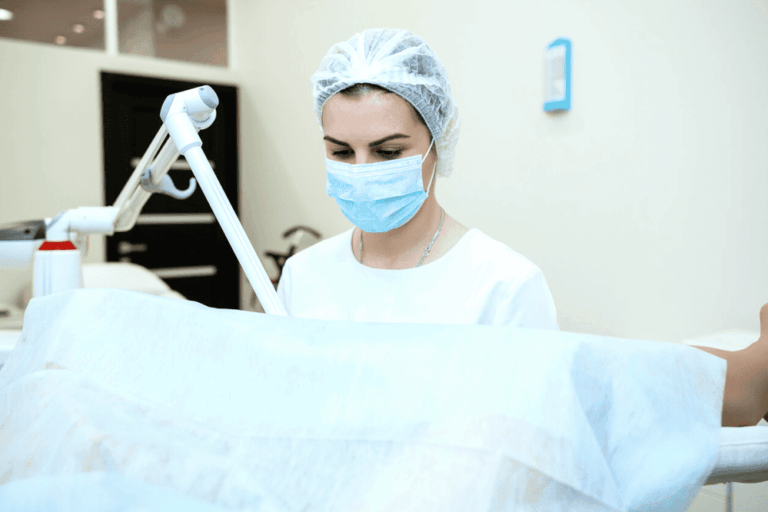
Перед тем как лечить бородавки у ребенка, нужно подтвердить диагноз. Дерматолог осматривает ребенка, определяет разновидность новообразований с помощью дерматоскопа (увеличительного прибора). Процедура эта совершенно безболезненна.
При множественных образованиях на коже потребуется сдать кровь для определения штамма папилломавируса и его активности. На основании полученных данных дерматолог или терапевт выбирают метод лечения бородавок у детей.
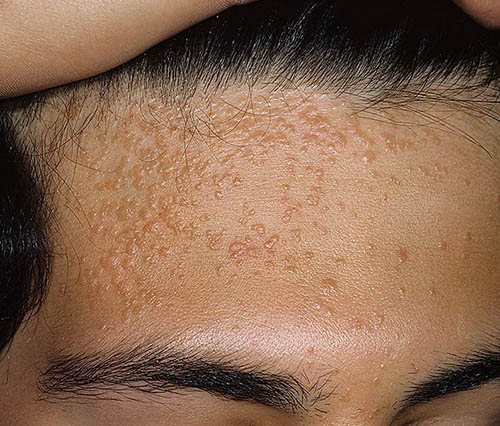
Лечение бородавоки
Решение, как избавиться от бородавки у ребенка, должен принимать врач. Самостоятельное удаление патологически разросшихся участков опасно распространением инфекции на незараженные участки кожи.
В настоящее время удаление бородавок возможно различными путями:
хирургический
электрокоагуляция
криодеструкция
лазерный
Перед тем как убрать бородавку у ребенка, врач назначает препараты для укрепления иммунитета и снижения вирусной активности. Полностью уничтожить вирус нельзя: он остается в организме на всю жизнь.