Очаговая алопеция — причины, симптомы и лечение
Очаговая алопеция — это форма облысения, при которой на голове или других участках кожи появляются зоны с полным отсутствием волос. Они чередуются с участками сохранённого волосяного покрова. Это состояние редко приводит к тотальному облысению, но вызывает серьёзный косметический дискомфорт. Основной пусковой механизм — стресс. Заболевание встречается как у мужчин, так и у женщин, а также у детей.
Симптомы очаговой алопеции
- Наличие округлых или овальных «гнёзд» облысения;
- Волосы по краям очагов легко выпадают при потягивании;
- Белые утолщения на концах волос;
- Возможное слияние очагов в более обширные зоны поражения.
Если эти признаки отсутствуют, заболевание перешло в стадию стабилизации.
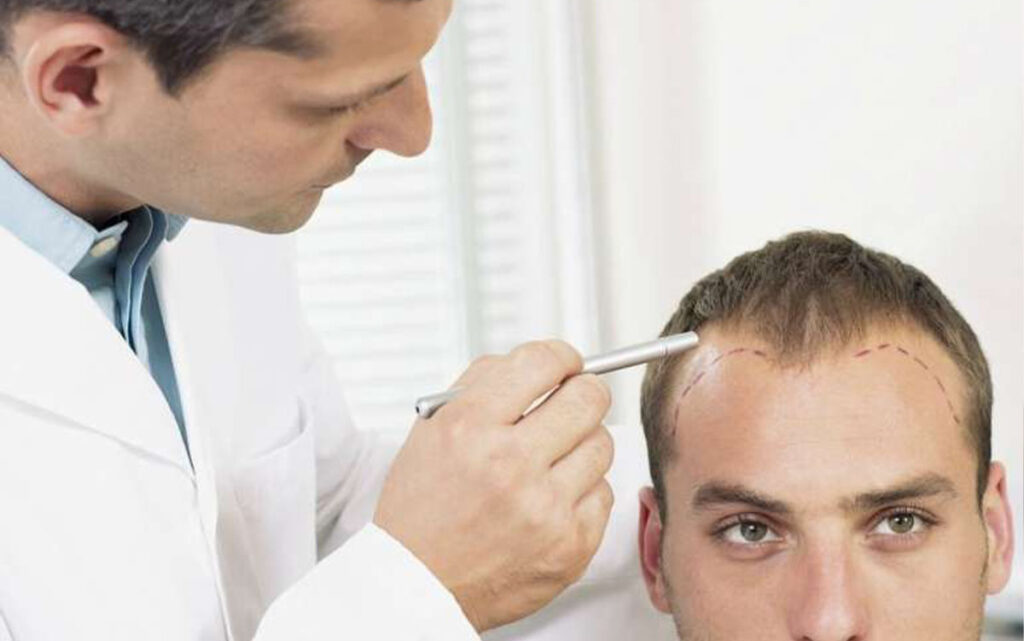
Диагностика
Диагноз ставится врачом-трихологом на основании визуального осмотра и специальных тестов:
- Потягивание волоса — для проверки прочности фолликула;
- Анализы крови — определение уровня Т- и В-лимфоцитов;
- Микроскопия волоса — для исключения грибковых поражений;
- Биопсия кожи — исключение аутоиммунных заболеваний (красная волчанка, саркоидоз и др.);
- Спектральный анализ волос — оценка баланса микроэлементов.
Лечение очаговой алопеции
- Регулярное мытьё головы с использованием нейтральных шампуней без агрессивных компонентов;
- Назначение витаминных комплексов и микроэлементов для стимуляции роста волос;
- Комплексный подход — устранение стрессов, коррекция иммунитета, местные препараты.
Замечаете участки выпадения волос?
Не ждите, пока очаги увеличатся! В нашей клинике вы получите точную диагностику и индивидуальный план восстановления роста волос. Эффективное лечение начинается с визита к специалисту.
📞 Звоните прямо сейчас: +99899 301-33-30